LinkedList(链表)
LinkedList 是用链表结构存储数据的,很适合数据的动态插入和删除,但随机访问和遍历的速度就比较慢。另外,它还提供了 List 接口中没有定义的方法,专门用于操作表头和表尾元素,可以当作堆栈、队列和双向队列使用。
源码分析
Node 是 LinkedList 的私有内部类,是 LinkedList 的核心,是 LinkedList 中用来存储节点的类,E 符号位泛型,属性 item 位当前元素,next 为指向当前节点的下一个节点,prev 为指向当前节点的上一个节点,是一种双向集合结构(双向链表)。
private static class Node<E> {
// 当前节点元素
E item;
// 下一个节点元素
Node<E> next;
// 上一个节点元素
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}属性
// 集合长度
transient int size = 0;
/**
* 头节点
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* 尾节点
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;构造方法
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
* 构造一个空的链表
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
* 构造一个列表,该列表包含指定集合的元素,其顺序由集合的迭代器返回。
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}add(E e)
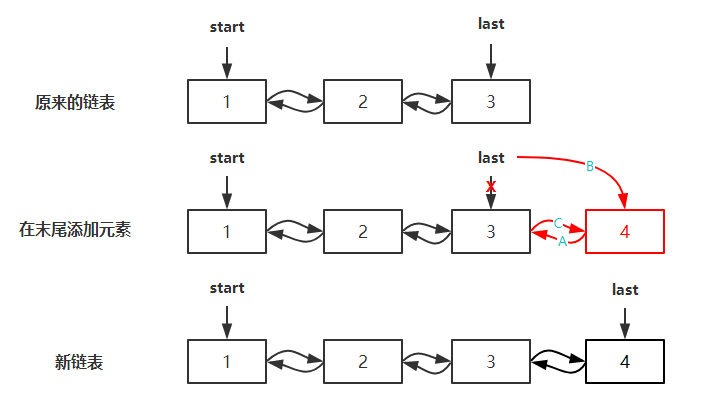
将指定的元素添加到集合链表的末尾,该方法和 addLast 方法的作用一样,主要是通过 LinkLast 方法来实现插入到末尾的,步骤如图所示:
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
* 将元素添加到集合的末尾
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #add}.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}addFirst(E e)
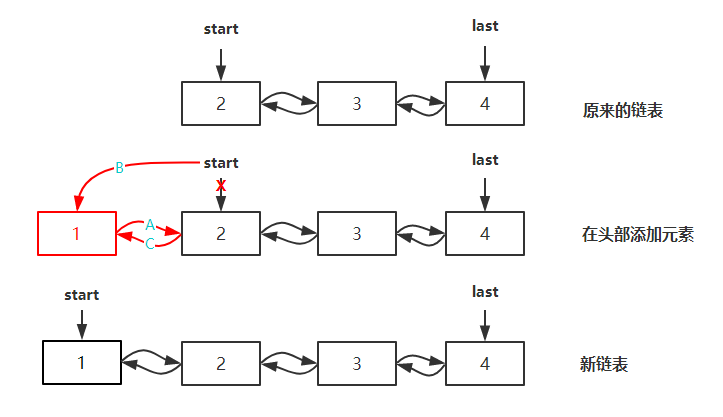
将元素添加到集合的头部,主要通过调用 LinkFirst 方法来实现,步骤如下图所示:
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* Links e as first element.
*/
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}add(int index, E element)
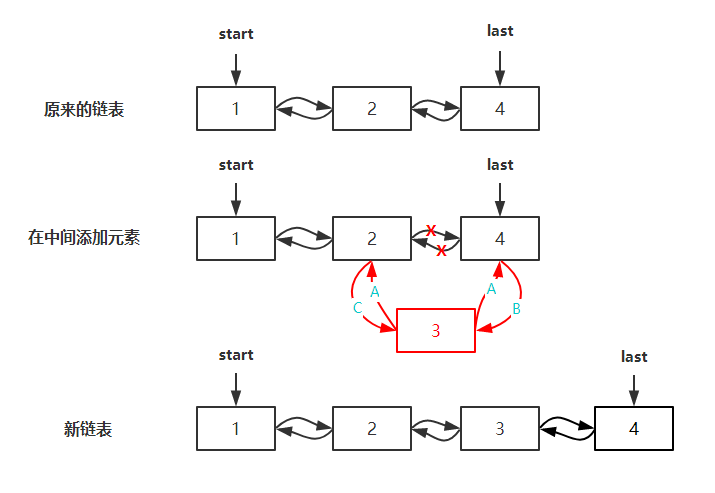
将指定的元素插入集合中的指定位置。将当前在该位置的元素(如果有的话)和任何后续的元素向右移位。在集合中间插入元素的平均时间复杂度为 O(1),该方式主要通过 node(int index) 方法找到对应位置的节点,再通过 linkBefore(E e, Node succ) 方法进行插入,在集合中间插入的步骤如图所示:
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an
* iterator or an add operation.
*/
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
/**
* Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message.
* Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code,
* this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs.
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}remove()
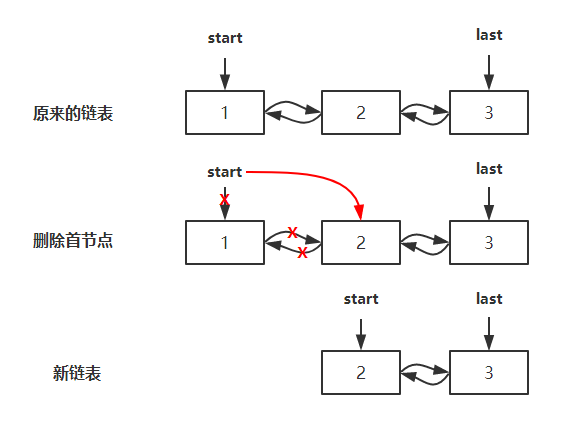
删除集合的第一个节点,并返回该元素,和 removeFirst 方法的作用一样,主要通过 unlinkFirst 方法实现删除头节点,并返回头节点的值,删除节点时将对应的节点值和节点的值指向都置为了 null,方便 GC 回收。删除步骤如图所示:
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* Removes and returns the first element from this list.
*
* @return the first element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null first node f.
* 删除不为 null 的首节点
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}removeLast()
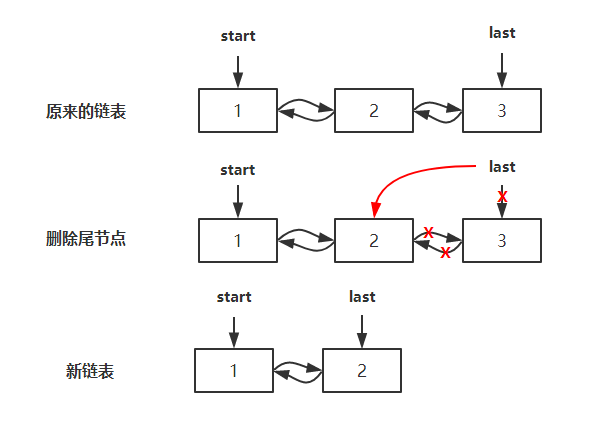
删除集合的最后一个节点,并返回该元素,主要通过 unlinkLast 方法实现删除尾节点,并返回尾节点的值,删除步骤如下图:
/**
* Removes and returns the last element from this list.
*
* @return the last element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null last node l.
*/
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}remove(int index)
删除集合中指定位置的元素。将所有后续元素向前移动,并返回从集合中删除的元素,先通过 node(int index) 方法获取指定位置的节点,再通过 unlink(Node x) 方法删除该节点并返回节点的值,步骤如下所示:
-Xn5BTXXv.png)
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any
* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).
* Returns the element that was removed from the list.
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of an existing element.
*/
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
/**
* Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message.
* Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code,
* this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs.
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}get(int index)
返回集合中指定位置的元素,现检查下标是否越界,再通过 node(index) 方法取到对应下标的节点,该节点的 item 属性即为对应的值。
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
/**
* Returns the first element in this list.
*
* @return the first element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
/**
* Returns the last element in this list.
*
* @return the last element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}node(int index)
返回指定元素索引处的(非空)元素,很多方法都会涉及到该方法。
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}offer(E e)
将指定的元素添加到集合的尾部,该方法的作用和 add(E e),addLast(E e) 一样。当使用容量受限的双端队列时,此方法通常比 add 方法更可取,当超出队列容量时,改方法返回 false,而 add 方法则会抛出异常。
/**
* Adds the specified element as the tail (last element) of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @since 1.5
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the front of this list.
*
* @param e the element to insert
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerFirst})
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this list.
*
* @param e the element to insert
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerLast})
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}poll()
删除集合的头节点,该方法的作用和 remove() 一样,不过当两个方法对空集合使用时,remove() 方法会抛出异常,而 poll() 方法会返回 null。
pollFirst() 方法和 poll() 方法的作用一样,当集合为空时返回 null。
poolLast() 方法和 removeLast() 方法的作用一样,步过当集合为空时,pollLast() 方法返回 null,removeLast() 方法会抛出异常。
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E poll() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the first element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} if
* this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the last element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} if
* this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}peek()
peek() 方法的作用和 getFirst() 方法一样,步过当集合为 null 时,peek() 方法返回 null,而 getFirst() 方法会抛出异常。
peekFirst() 方法的作用和 peek() 一样,peekLast() 方法的作用和 removeLast() 方法一样,不过该方法遇到空集合也是返回 null。
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E peek() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the first element of this list, or {@code null}
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E peekFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the last element of this list, or {@code null}
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E peekLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}总结
- LinkedList 底层是基于链表的,查找节点的平均时间复杂度是 O(n),首位增加和删除节点的时间复杂度是 O(1)。
- LinkedList 适合读少写多的情况,ArrayList 适合读多写少的情况。
- LinkedList 作为队列使用时,可以通过 offer/poll/peek 来代替 add/remove/get 等方法,这些方法在遇到空集合或队列容量满的情况下不会抛出异常。
