TreeSet
大约 8 分钟
TreeSet 是使用二叉树的原理对新的 add() 的对象按照指定的顺序排序(升序、降序),每增加一个对象就会进行排序,将对象插入到二叉树指定的位置。
Integer 和 String 对象都可以进行默认的 TreeSet 排序,而自定义的对象是不可以的,自定义的类必须实现 Comparable 接口,并且重写相应的 compareTo() 函数,才可以正常使用。
在覆写 compare() 函数时,要返回相应的值才能使 TreeSet 按照一定的规则排序。比较此对象与指定对象的顺序。如果改对象小于、等于或大于指定对象,则分别返回负整数、零或正整数。
继承关系
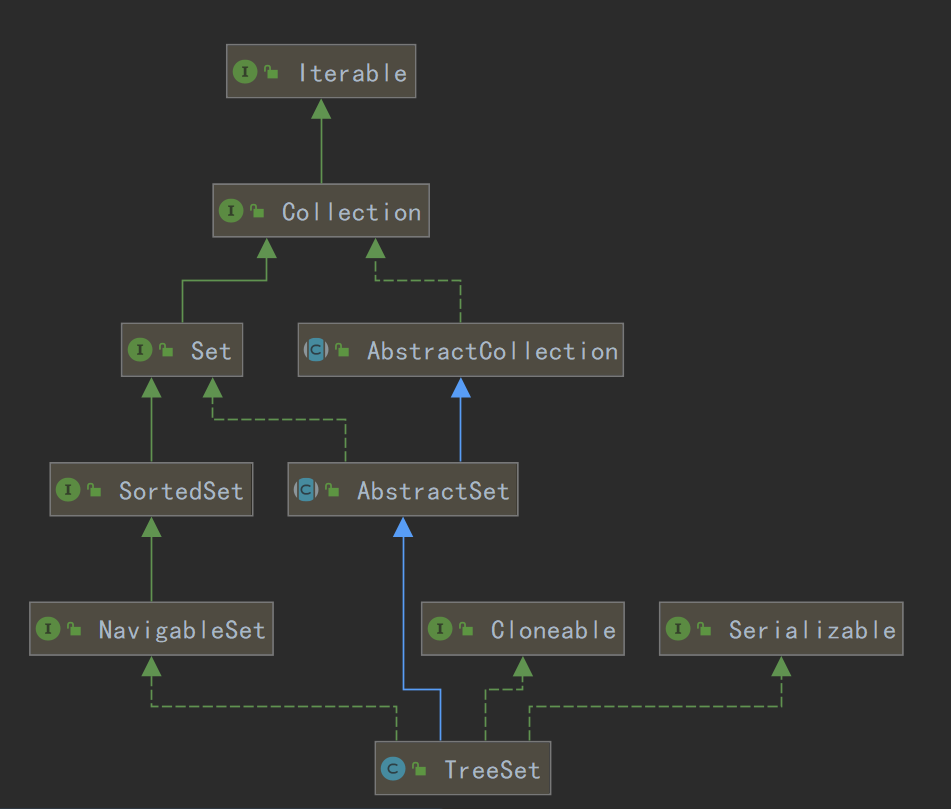
- 实现了 Serializable 接口,支持对象序列化。
- 实现了 Cloneable 接口,意味着它能被克隆。
- 实现了 Iterable 接口,即能用 foreach 迭代器遍历集合元素。
- 实现了 NavigableSet 接口,意味着它支持一系列的导航方法,比如查找与指定目标最匹配项。
- 继承了 AbstractSet,AbstractSet 实现了 set,所以它是一个 Set 集合,不包含满足 element1.equals(element2) 的元素树,不重复,并且最后包含一个 null。
源码分析
基本属性
/**
* The backing map.
*/
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();构造方法及初始化
/**
* Constructs a set backed by the specified navigable map.
*
* 底层维护其实是一个 Navigable Map
*/
TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m) {
this.m = m;
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty tree set, sorted according to the
* natural ordering of its elements. All elements inserted into
* the set must implement the {@link Comparable} interface.
* Furthermore, all such elements must be <i>mutually
* comparable</i>: {@code e1.compareTo(e2)} must not throw a
* {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1} and
* {@code e2} in the set. If the user attempts to add an element
* to the set that violates this constraint (for example, the user
* attempts to add a string element to a set whose elements are
* integers), the {@code add} call will throw a
* {@code ClassCastException}.
*
* 构造一个新的空树集,并根据其元素的自然顺序对其进行排序。 插入集合中的所有元素都必须实现Comparable接口。
* 此外,所有这些元素必须相互可比较(即都重写了 compareTo() 方法): e1.compareTo(e2)不得为集合中的任何元素e1和e2引发ClassCastException 。
* 如果用户尝试向违反此约束的集合中添加元素(例如,用户尝试向其元素为整数的集合中添加字符串元素),则add调用将抛出ClassCastException 。
*/
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
/**
* Constructs a new, empty tree set, sorted according to the specified
* comparator. All elements inserted into the set must be <i>mutually
* comparable</i> by the specified comparator: {@code comparator.compare(e1,
* e2)} must not throw a {@code ClassCastException} for any elements
* {@code e1} and {@code e2} in the set. If the user attempts to add
* an element to the set that violates this constraint, the
* {@code add} call will throw a {@code ClassCastException}.
*
* @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this set.
* If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable natural
* ordering} of the elements will be used.
*
* 构造一个新的空树集,该树集根据指定的比较器进行排序。
* 插入到集合中的所有元素必须与指定的比较器相互比较: comparator.compare(e1, e2)不得对集合中的任何元素e1和e2抛出ClassCastException 。
* 如果用户尝试将违反此约束的元素添加到集合中,则add调用将抛出ClassCastException 。
*/
public TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
this(new TreeMap<>(comparator));
}
/**
* Constructs a new tree set containing the elements in the specified
* collection, sorted according to the <i>natural ordering</i> of its
* elements. All elements inserted into the set must implement the
* {@link Comparable} interface. Furthermore, all such elements must be
* <i>mutually comparable</i>: {@code e1.compareTo(e2)} must not throw a
* {@code ClassCastException} for any elements {@code e1} and
* {@code e2} in the set.
*
* @param c collection whose elements will comprise the new set
* @throws ClassCastException if the elements in {@code c} are
* not {@link Comparable}, or are not mutually comparable
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*
* 构造一个包含指定集合中元素的新树集,并根据其元素的自然顺序对其进行排序。 插入集合中的所有元素都必须实现Comparable接口。
* 此外,所有这些元素必须相互可比较: e1.compareTo(e2)不得为集合中的任何元素e1和e2引发ClassCastException 。
*/
public TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
/**
* Constructs a new tree set containing the same elements and
* using the same ordering as the specified sorted set.
*
* @param s sorted set whose elements will comprise the new set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified sorted set is null
*
* 构造一个新的树集,其中包含与指定的排序集相同的元素,并使用相同的顺序。
*/
public TreeSet(SortedSet<E> s) {
this(s.comparator());
addAll(s);
}- TreeSet 是基于 TreeMap 实现的。
- TreeSet 中的元素支持 2 种排序方式:自然排序或者根据创建 TreeSet 时提供的 Comparator 进行排序。这取决于使用的构造方法。
- TreeSet 为基本操作(add、remove 和 contains)提供受保证的 log(n) 时间开销。
- TreeSet 是非同步的。它的 iterator 方法返回的迭代器是 fail - fast 的。
常用方法
/**
* Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present.
* More formally, adds the specified element {@code e} to this set if
* the set contains no element {@code e2} such that
* <tt>(e==null ? e2==null : e.equals(e2))</tt>.
* If this set already contains the element, the call leaves the set
* unchanged and returns {@code false}.
*
* @param e element to be added to this set
* @return {@code true} if this set did not already contain the specified
* element
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified object cannot be compared
* with the elements currently in this set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
*
* 如果指定的元素尚不存在,则将其添加到该集合中。 更正式地讲,如果集合中不包含任何元素e2 ,
* 则将指定的元素e添加到该集合中,使得(e == null?e2 == null:e.equals(e2)) 。
* 如果此集合已经包含该元素,则调用将使该集合保持不变,并返回false 。
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
/**
* Removes the specified element from this set if it is present.
* More formally, removes an element {@code e} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>,
* if this set contains such an element. Returns {@code true} if
* this set contained the element (or equivalently, if this set
* changed as a result of the call). (This set will not contain the
* element once the call returns.)
*
* @param o object to be removed from this set, if present
* @return {@code true} if this set contained the specified element
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified object cannot be compared
* with the elements currently in this set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
* and this set uses natural ordering, or its comparator
* does not permit null elements
*
* 如果存在,则从此集合中删除指定的元素。 更正式地说,移除元素e满足(o == NULLé== NULL:o.equals(e)条),如果此set包含这样的元素。
* 如果此集合包含元素,则返回true (或者等效地,如果此集合由于调用而更改),则返回true 。 (一旦调用返回,此集合将不包含该元素。)
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return m.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this set.
* The set will be empty after this call returns.
*
* 从该集合中删除所有元素。 该调用返回后,该集合将为空。
*/
public void clear() {
m.clear();
}
/**
* Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this set.
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this set
* @return {@code true} if this set changed as a result of the call
* @throws ClassCastException if the elements provided cannot be compared
* with the elements currently in the set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null or
* if any element is null and this set uses natural ordering, or
* its comparator does not permit null elements
*
* 将指定集合中的所有元素添加到该集合中。
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
// Use linear-time version if applicable
if (m.size()==0 && c.size() > 0 &&
c instanceof SortedSet &&
m instanceof TreeMap) {
SortedSet<? extends E> set = (SortedSet<? extends E>) c;
TreeMap<E,Object> map = (TreeMap<E, Object>) m;
Comparator<?> cc = set.comparator();
Comparator<? super E> mc = map.comparator();
if (cc==mc || (cc != null && cc.equals(mc))) {
map.addAllForTreeSet(set, PRESENT);
return true;
}
}
return super.addAll(c);
}
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this set in ascending order.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this set in ascending order
*
* 以升序返回此集合中元素的迭代器。
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return m.navigableKeySet().iterator();
}
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this set in descending order.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this set in descending order
* @since 1.6
*
* 以降序返回此集合中元素的迭代器。
*/
public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {
return m.descendingKeySet().iterator();
}总结
- 不能有重复的元素;
- 具有排序功能;
- TreeSet中的元素必须实现Comparable接口并重写compareTo()方法,TreeSet判断元素是否重复 、以及确定元素的顺序 靠的都是这个方法;
- 对于java类库中定义的类,TreeSet可以直接对其进行存储,如String,Integer等,因为这些类已经实现了Comparable接口);
- 对于自定义类,如果不做适当的处理,TreeSet中只能存储一个该类型的对象实例,否则无法判断是否重复。
- 依赖于TreeMap,底层是TreeMap。
- 相对HashSet,TreeSet的优势是有序,劣势是相对读取慢。
TreeSet 与 HashSet
- 相同点:都是唯一不重复的 Set 集合
- 不同点:
- 底层结构:HashSet 是用 Hash 表来存储数据,而 TreeSet 是采用二叉平衡树来存储数据。
- 功能上:由于 TreeSet 是有序的 Set,可以使用 SortedSet 接口的 first()、last()等方法;但由于要排序,势必要影响速度;所以,在不需要顺序的情况下,使用 HashSet,在这方面使用 Hash 表存储数据的 HashSet 在速度上更胜一筹;如果需要顺序则使用 TreeSet。
TreeSet 与 HashMap
- 相同点:
- TreeMap 和 TreeSet 都是有序的集合。
- TreeMap 和 TreeSet 都是非同步集合,因此它们不能在多线程之间共享,不过可以使用方法 Collections.synchroinzedMap() 来实现同步。
- 运行速度都要比 Hash 集合满,它们内部对元素的操作时间复杂度为 O(logN),而 HashMap / HashSet 则为 O(1)。
- 不同点:
- 实现的接口不同,TreeSet 实现 Set 接口,而 TreeMap 实现 Map 接口。
- TreeSet 只存储一个对象,而 TreeMap 存储两个对象 key 和 value。
- TreeSet 种不能有重复对象,而 TreeMap 种可以存在。
